Image of the Week | Archive
These images have been sourced from across EOTEC DevNet community to showcase examples of how Earth Observations are used to inspire and educate the public, as well as assist scientists and decision-makers in their work. If you have a story to tell with satellite imagery – please submit it via this this FORM.
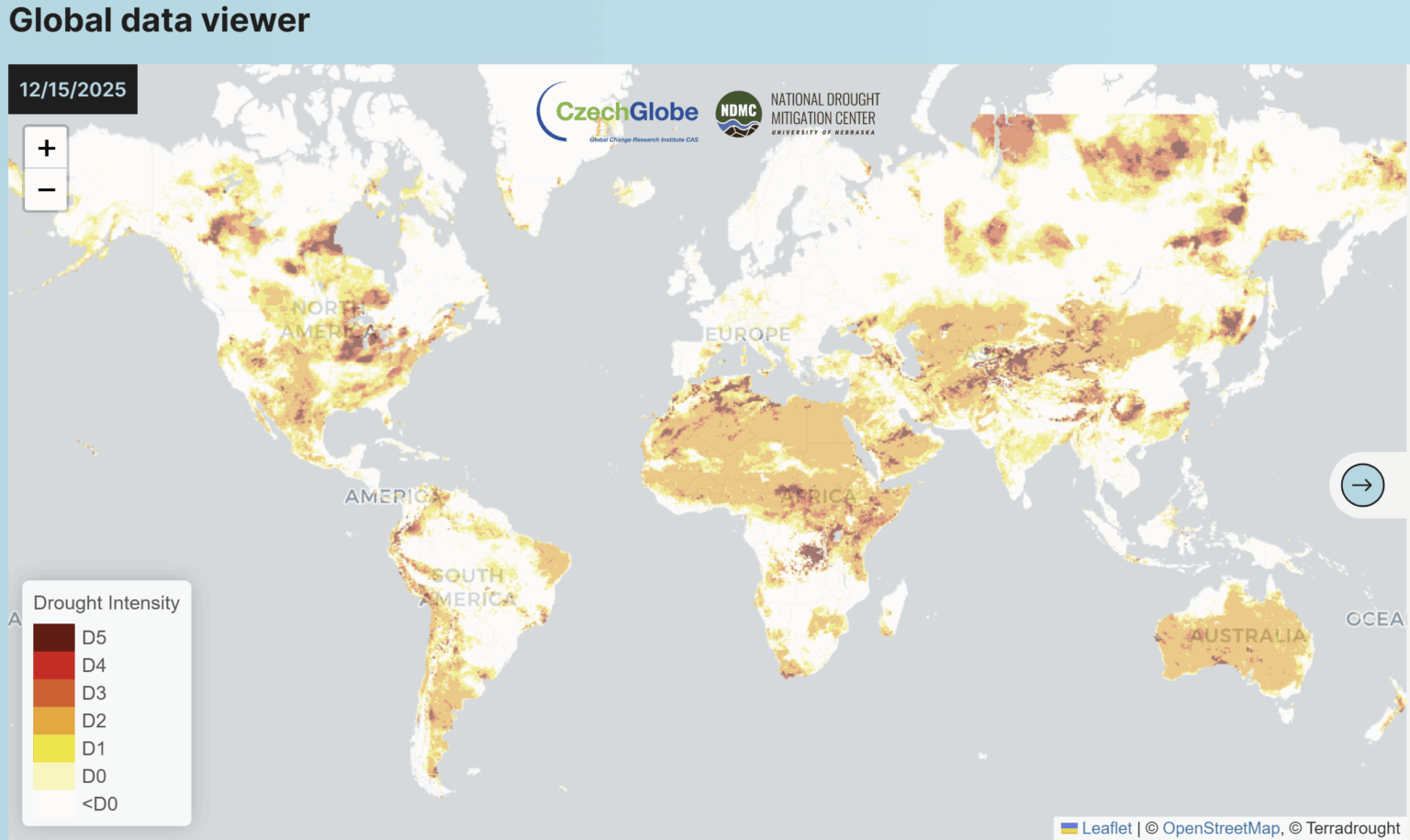
Heat and dryness in summer 2025–26 contributed to fire risk
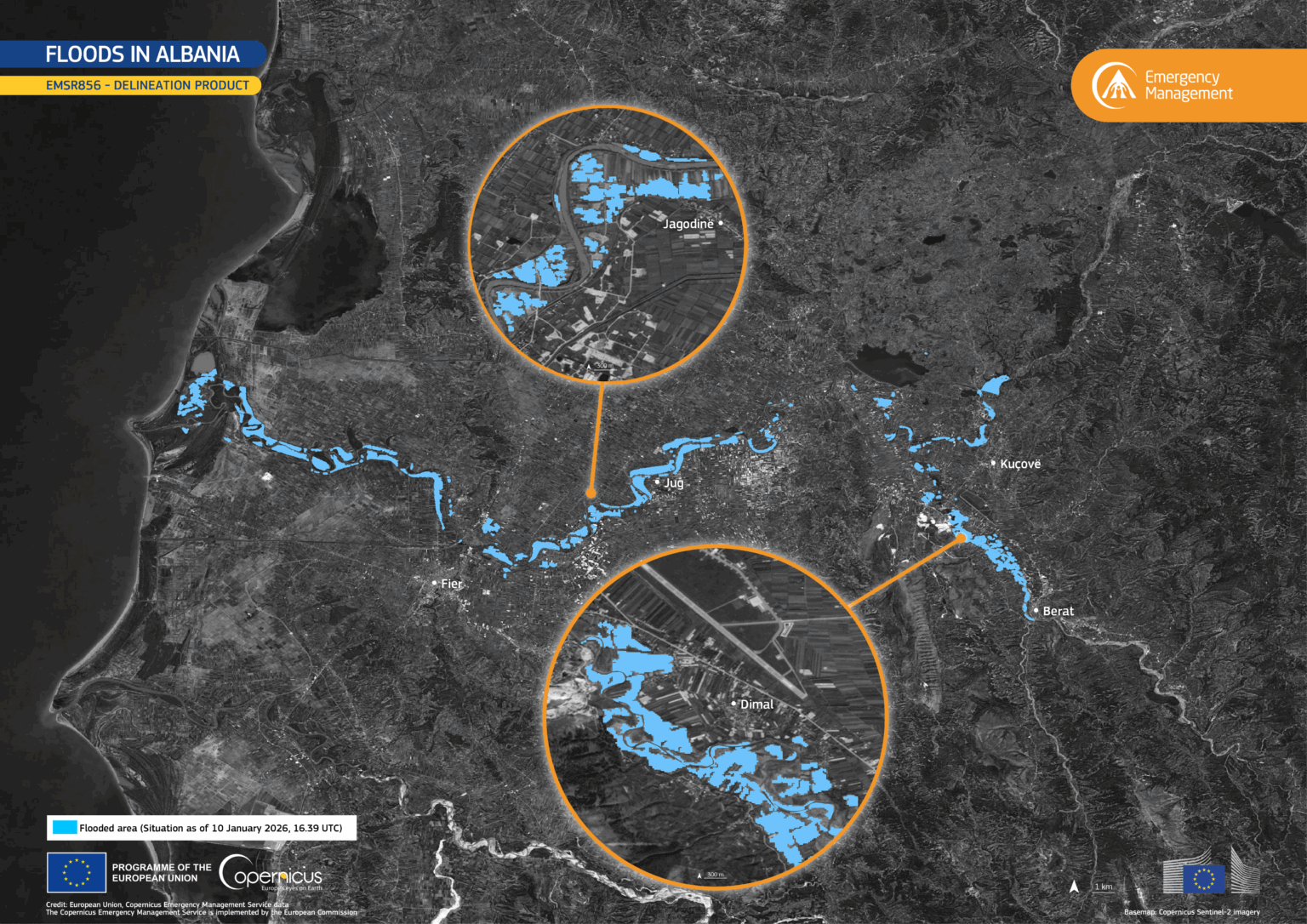
The first month of 2026 brought intense rainfall and cyclones to many corners of the globe, including central and western Albania.
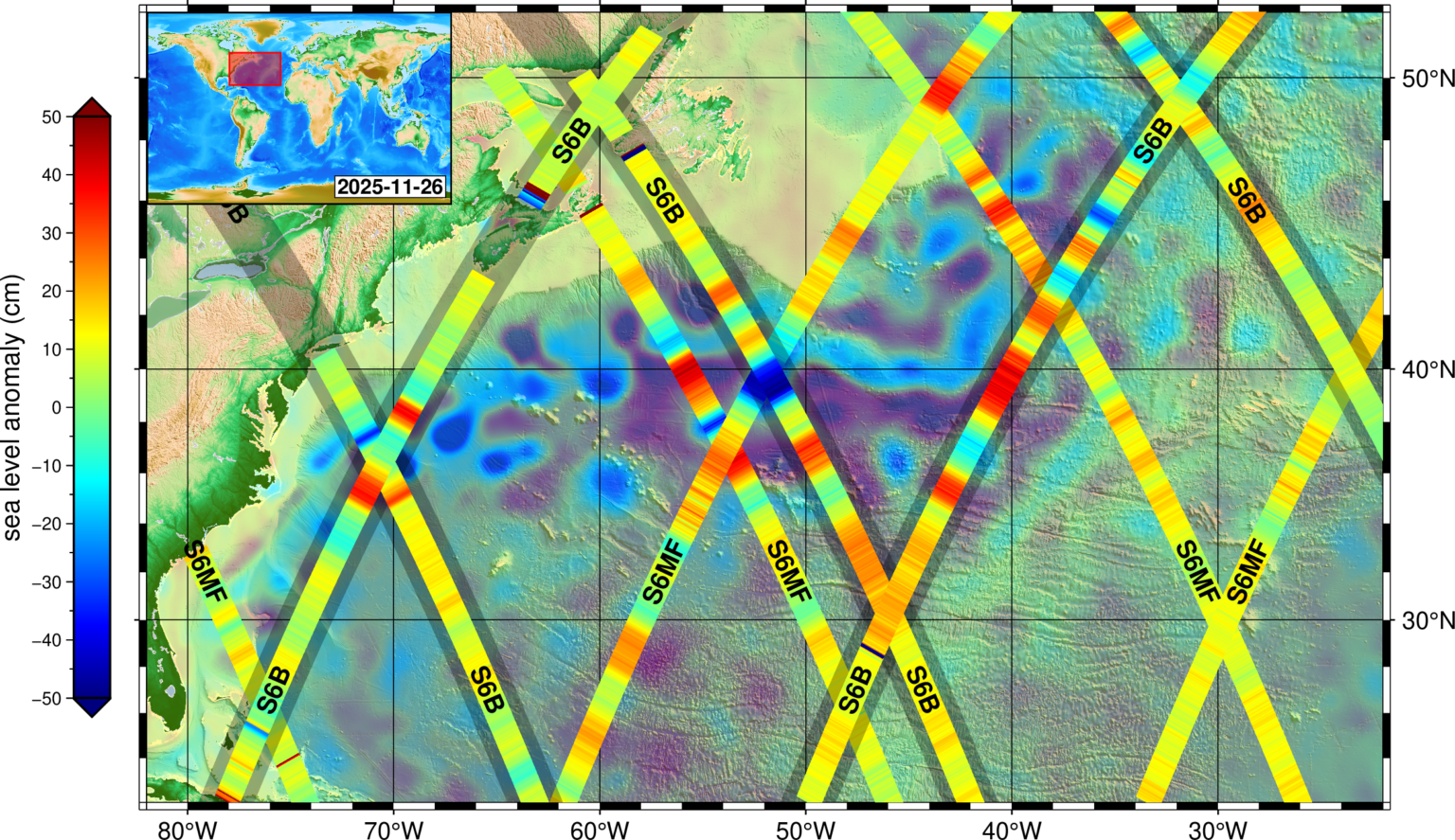
Sentinel-6B and Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich captured data on Nov. 26 of sea levels across a vast stretch of the Atlantic Ocean.
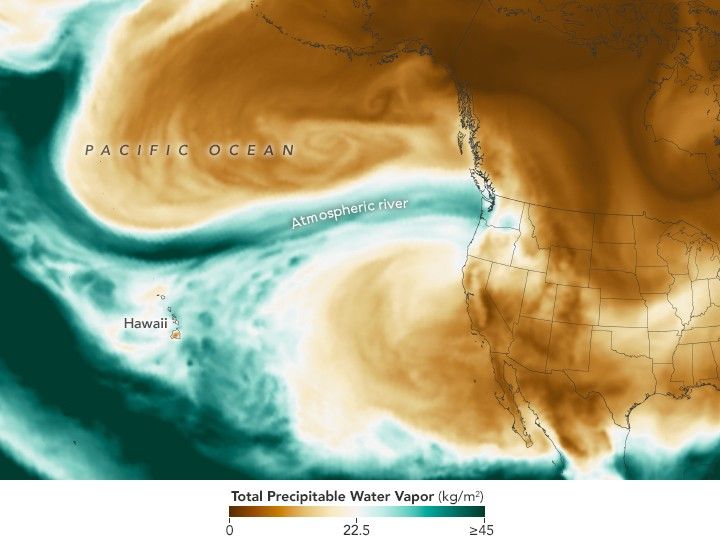
In the U.S. Pacific Northwest, a potent atmospheric river spurred waves of heavy rainfall that caused landslides and flooding.
This image shows the total precipitable water vapor in the atmosphere at 11:30 p.m. Pacific Time on December 10. It is derived from NASA’s GEOS (Goddard Earth Observing System)
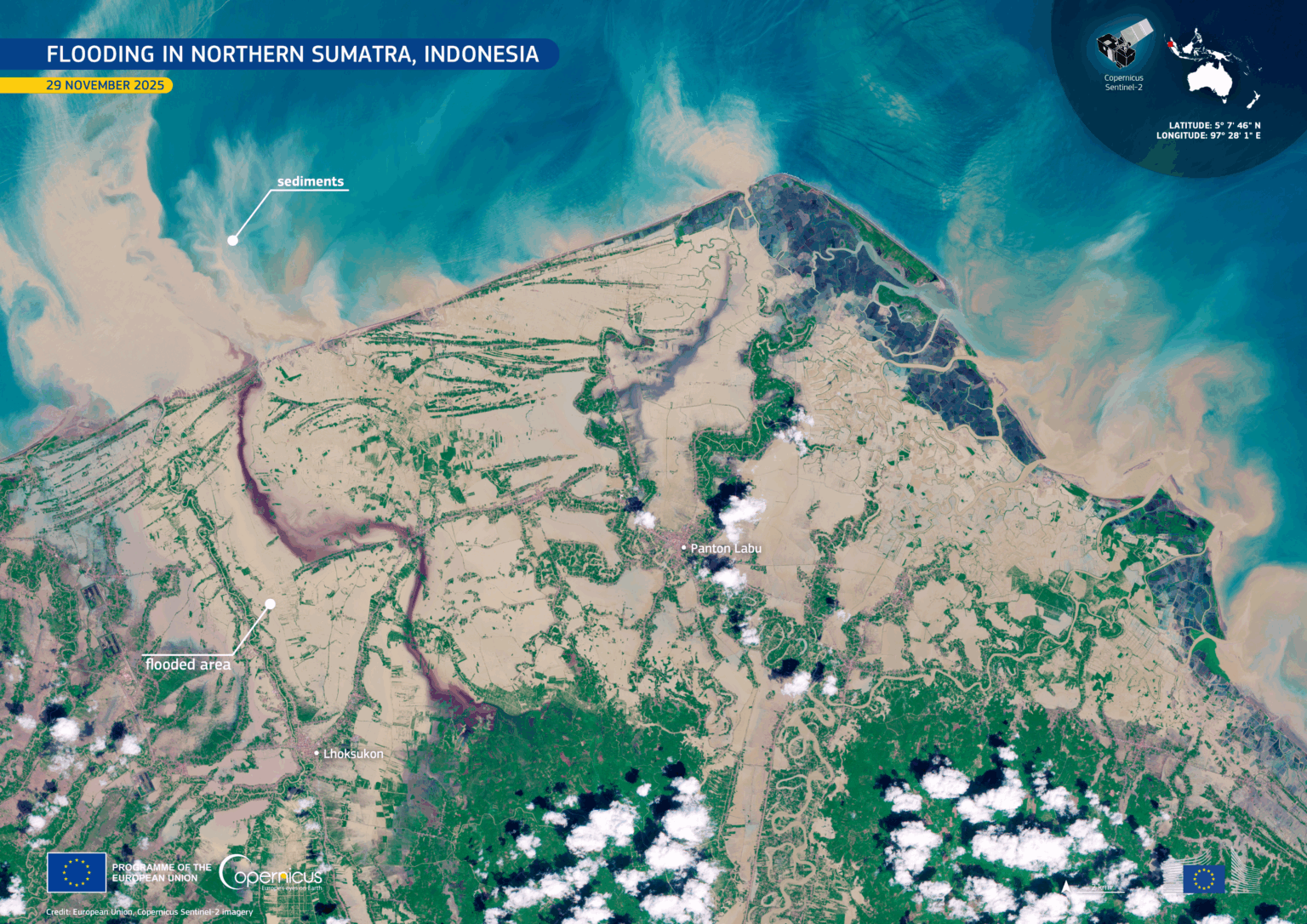
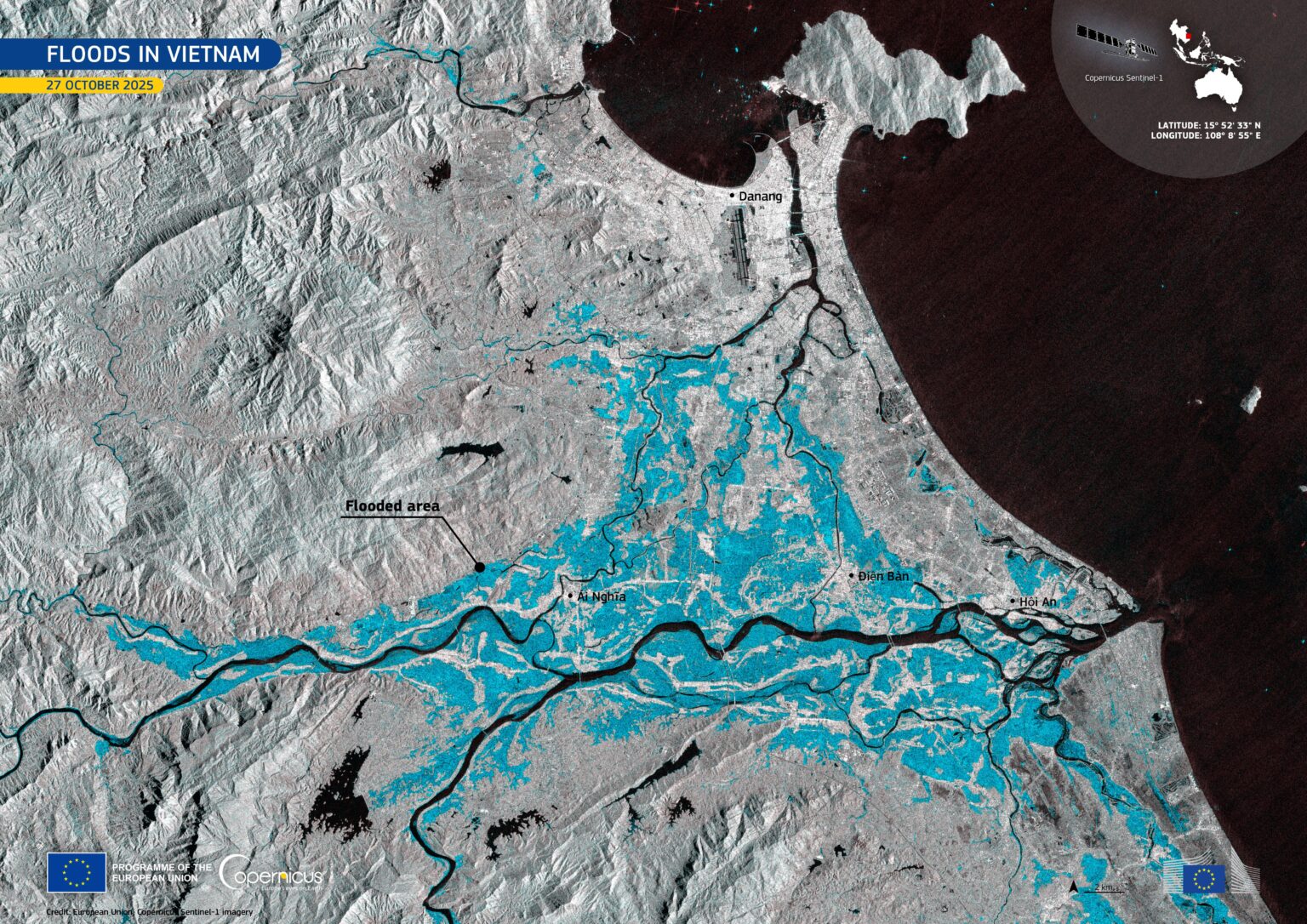
In late October 2025, severe flooding struck Vietnam after days of intense rainfall. In this image, flooded areas along the Vu Gia and Thu Bồn appear in blue tones. Open data from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellites provides cloud-penetrating radar imagery, which is essential for tracking flood extent and supporting timely emergency response.
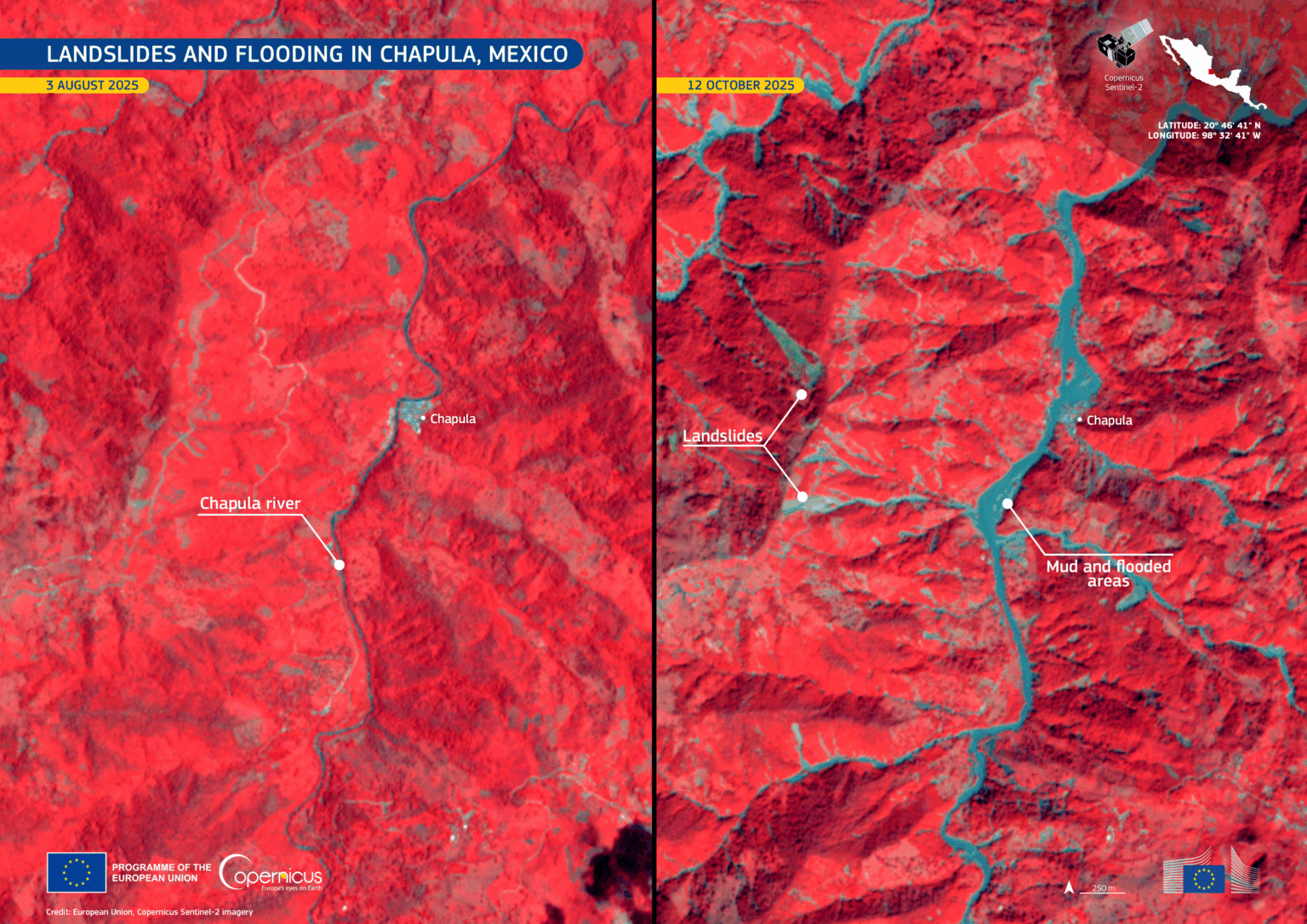
Satellite imagery captures the impact of torrential rains from tropical storms, which caused severe flooding and landslides in central and eastern Mexico.
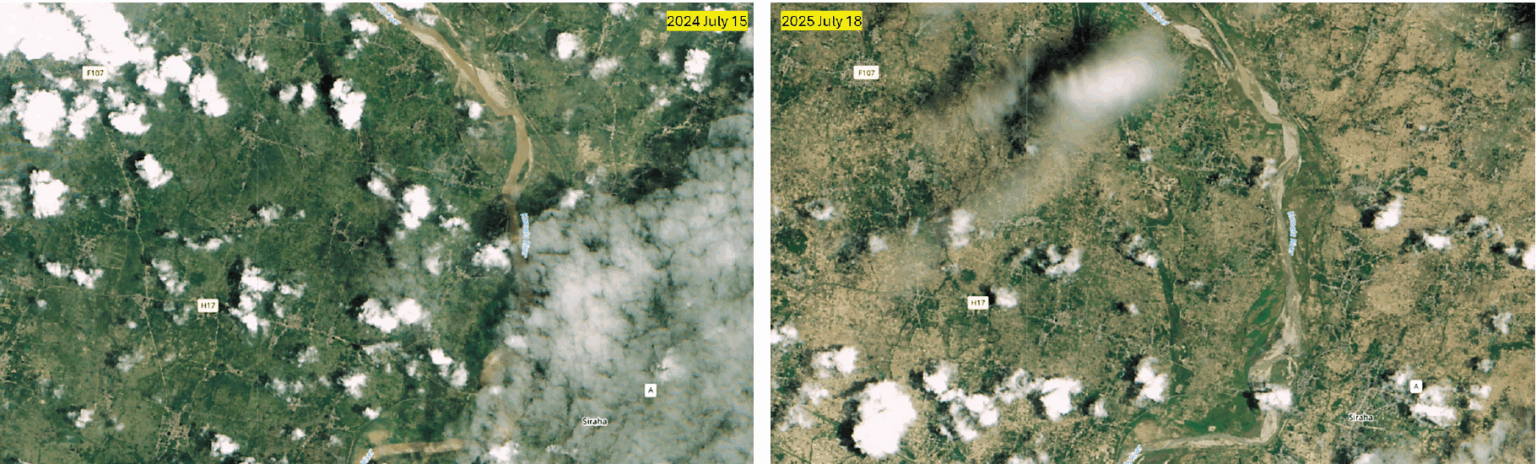
A region of Nepal better known for flooding has experienced a catastrophic drought.
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar Earth-observing satellite’s first images of our planet’s surface are in, and they offer a glimpse of things to come as the joint mission approaches full science operations later this year.
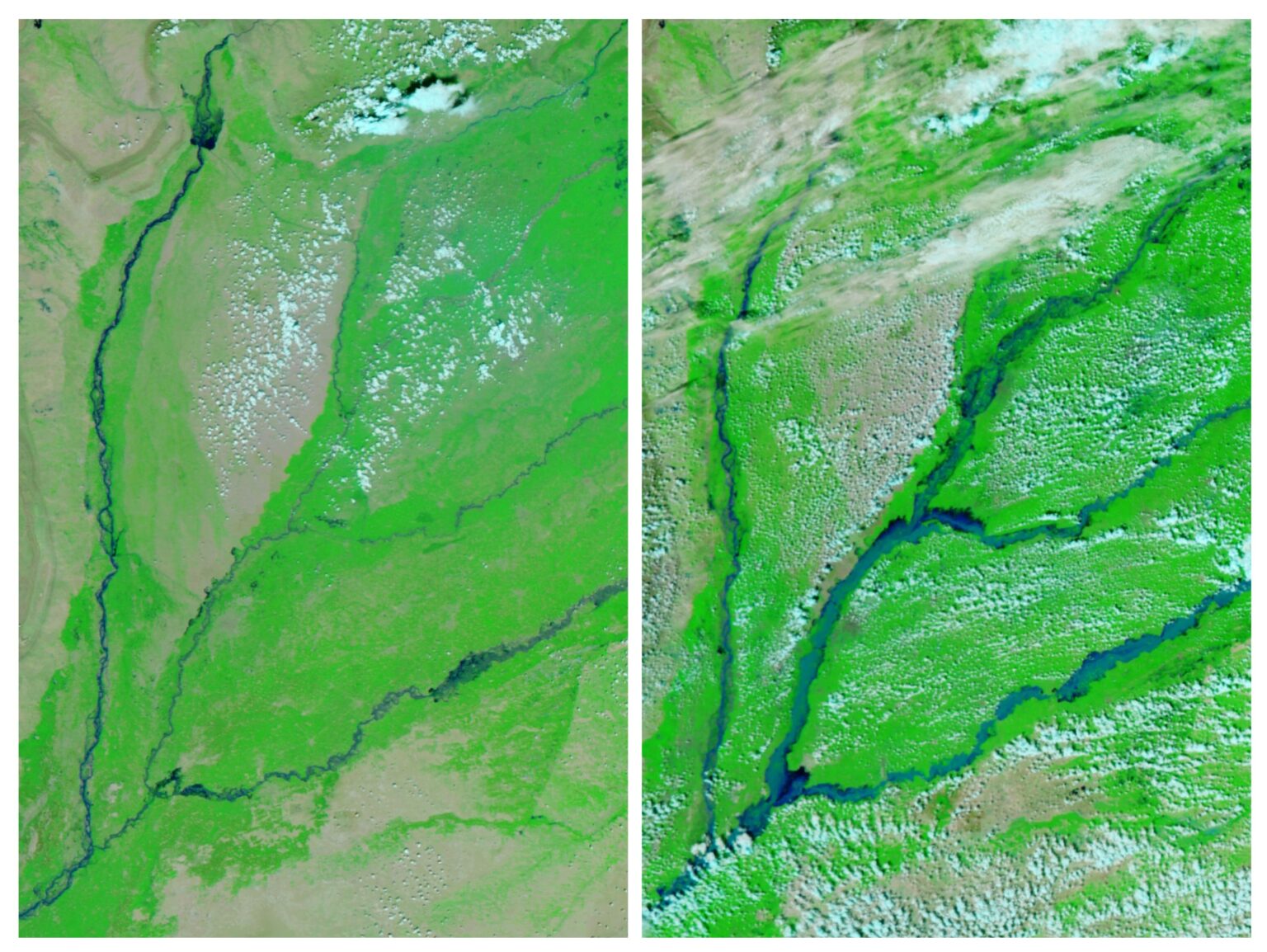
Extensive flooding in Pakistan has affected millions of people, destroyed infrastructure, inundated a large portion of the country’s agricultural land, and claimed hundreds of lives. The image on the right shows flooding along major rivers in the region on September 9, 2025. For comparison, the left image shows the area on the same day in 2023, when monsoon rainfall amounts were close to normal.
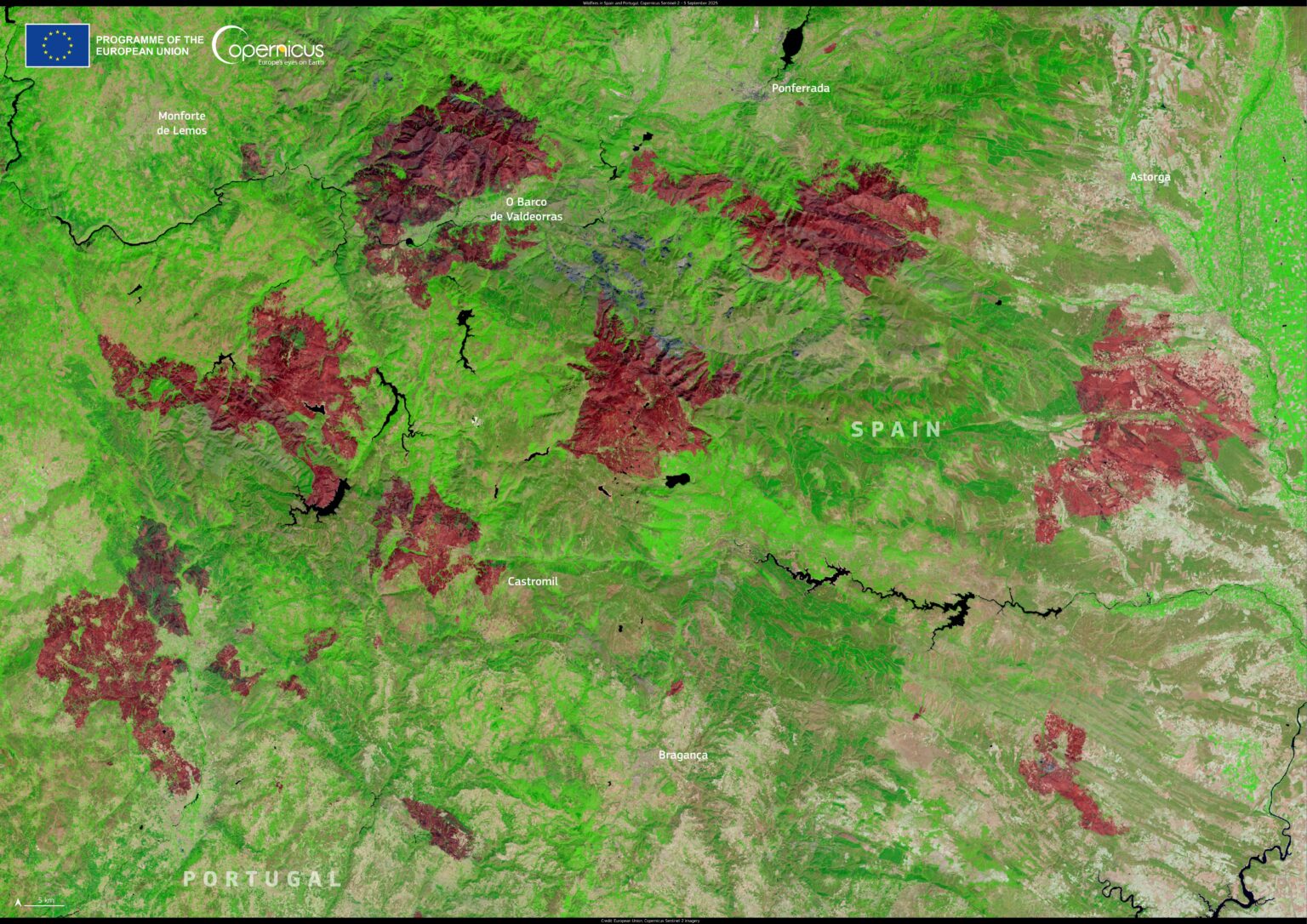
Wildfires along the Spain–Portugal border in August 2025, shown in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image from 5 September, left extensive burn scars around Castromil, O Barco de Valdeorras, and Bragança, providing vital data for post-fire recovery and protection efforts.
27 August is the first-ever World Lake Day, dedicated to tracking and protecting the health of millions of lakes around the globe.
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image from 13 August 2025 shows Lake Suchitlan, El Salvador’s largest wetland reservoir and a key source of the country’s hydropower.
Following the launch of Copernicus Sentinel-4A last month, the European Union successfully launched the Copernicus Sentinel-5A to further monitor air quality and emissions around the world.
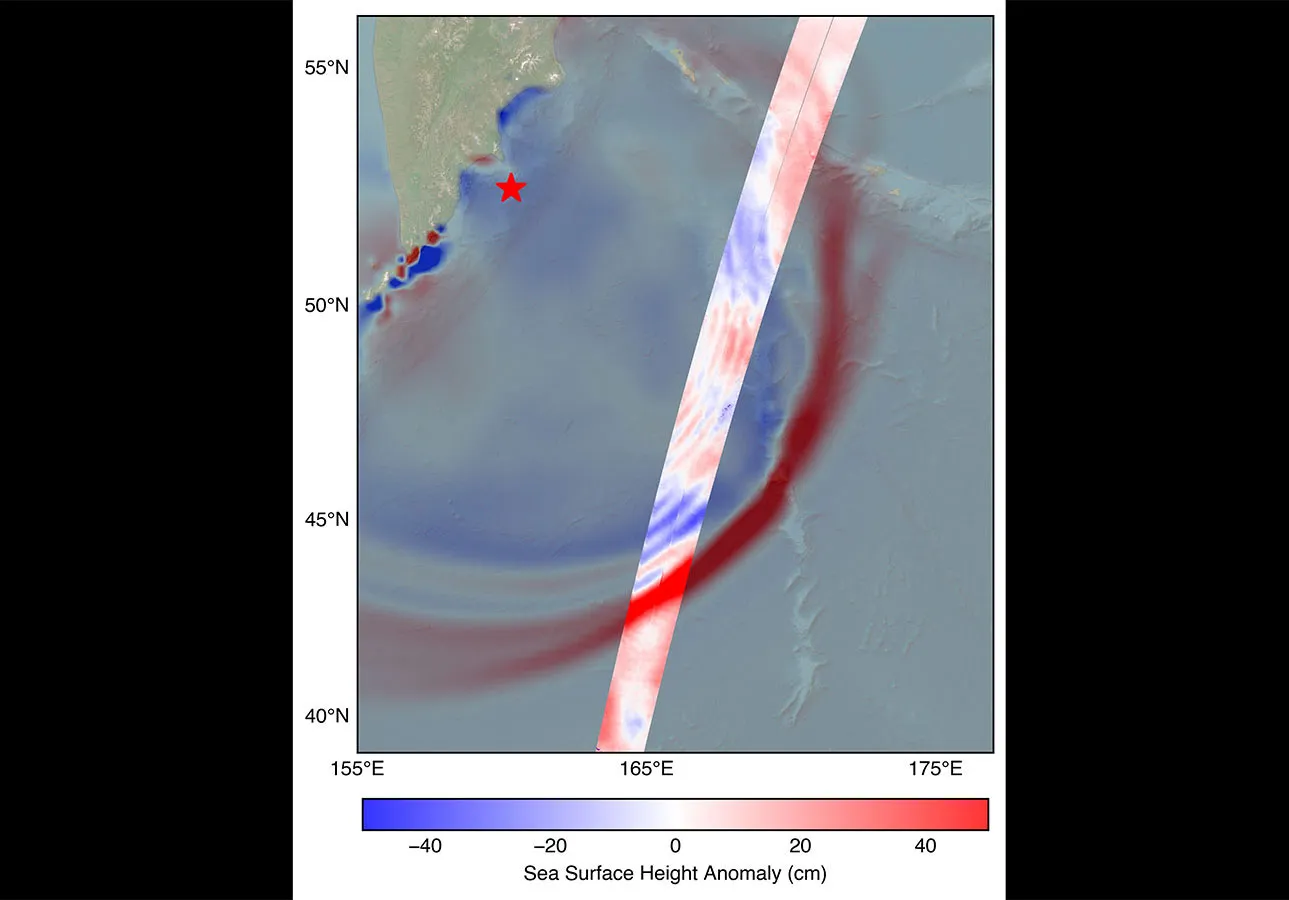
The SWOT (Surface Water and Ocean Topography) satellite captured the tsunami spawned by an 8.8 magnitude earthquake off the coast of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula on July 30, 11:25 a.m. local time. The satellite, a joint effort between NASA and the French space agency CNES (Centre National d’Études Spatiales), recorded the tsunami about 70 minutes after the earthquake struck.
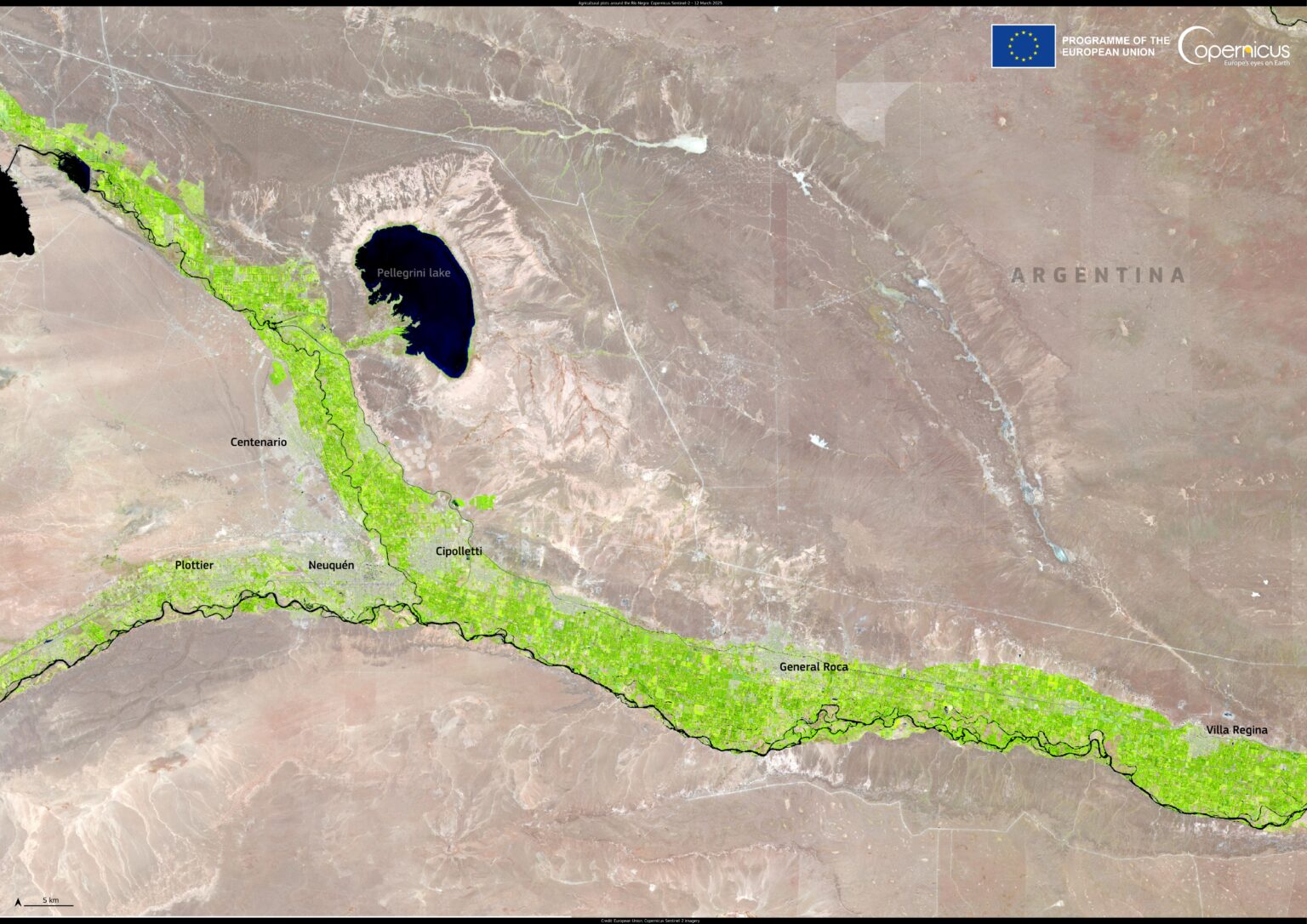
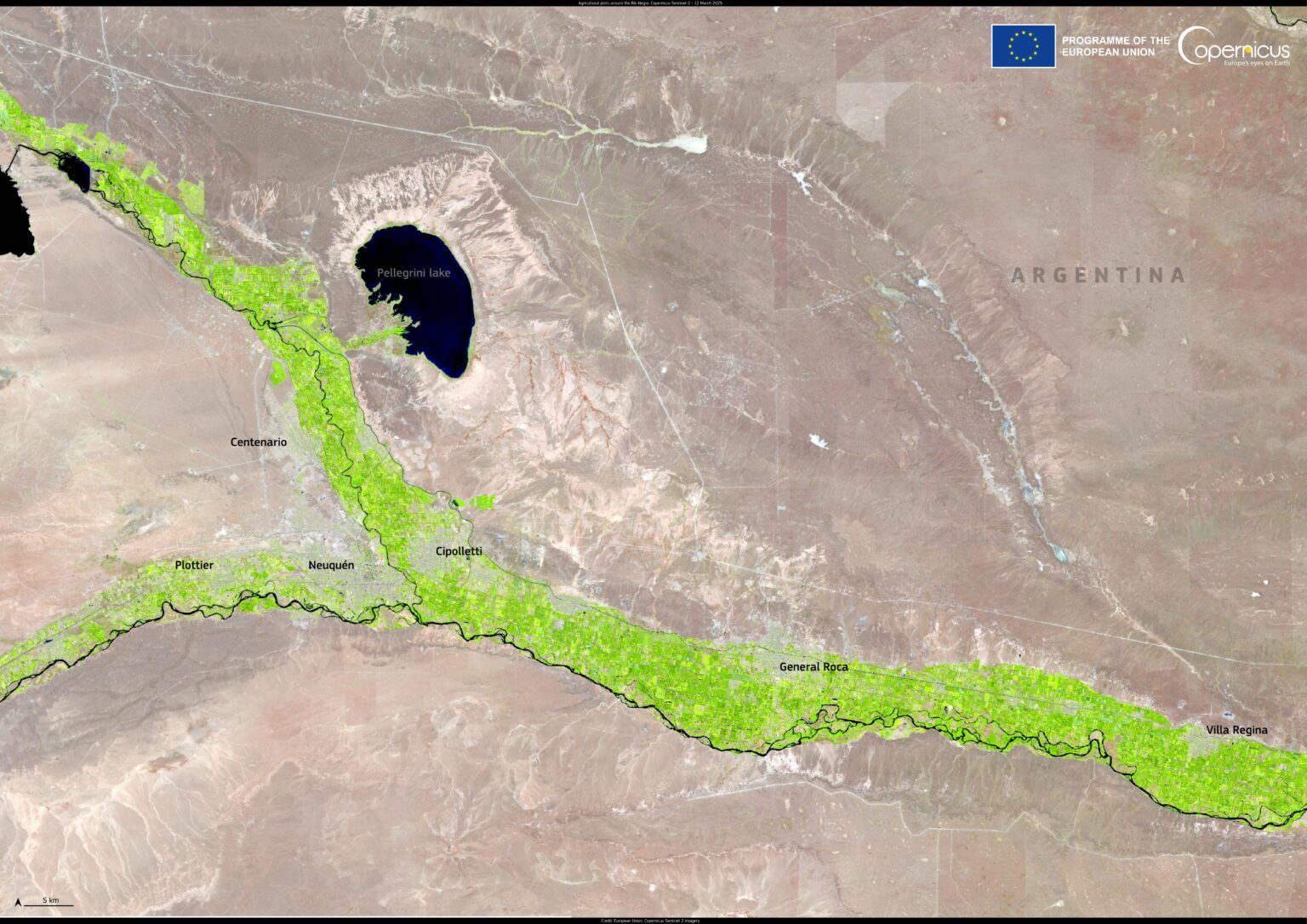
Stretching across the arid plains of northern Patagonia, the Alto Valle of the Río Negro is a remarkable agricultural oasis in Argentina. Despite the surrounding semi-desert landscape, this narrow strip thrives thanks to irrigation from the Río Negro River, supporting one of the country’s most productive fruit-growing regions.
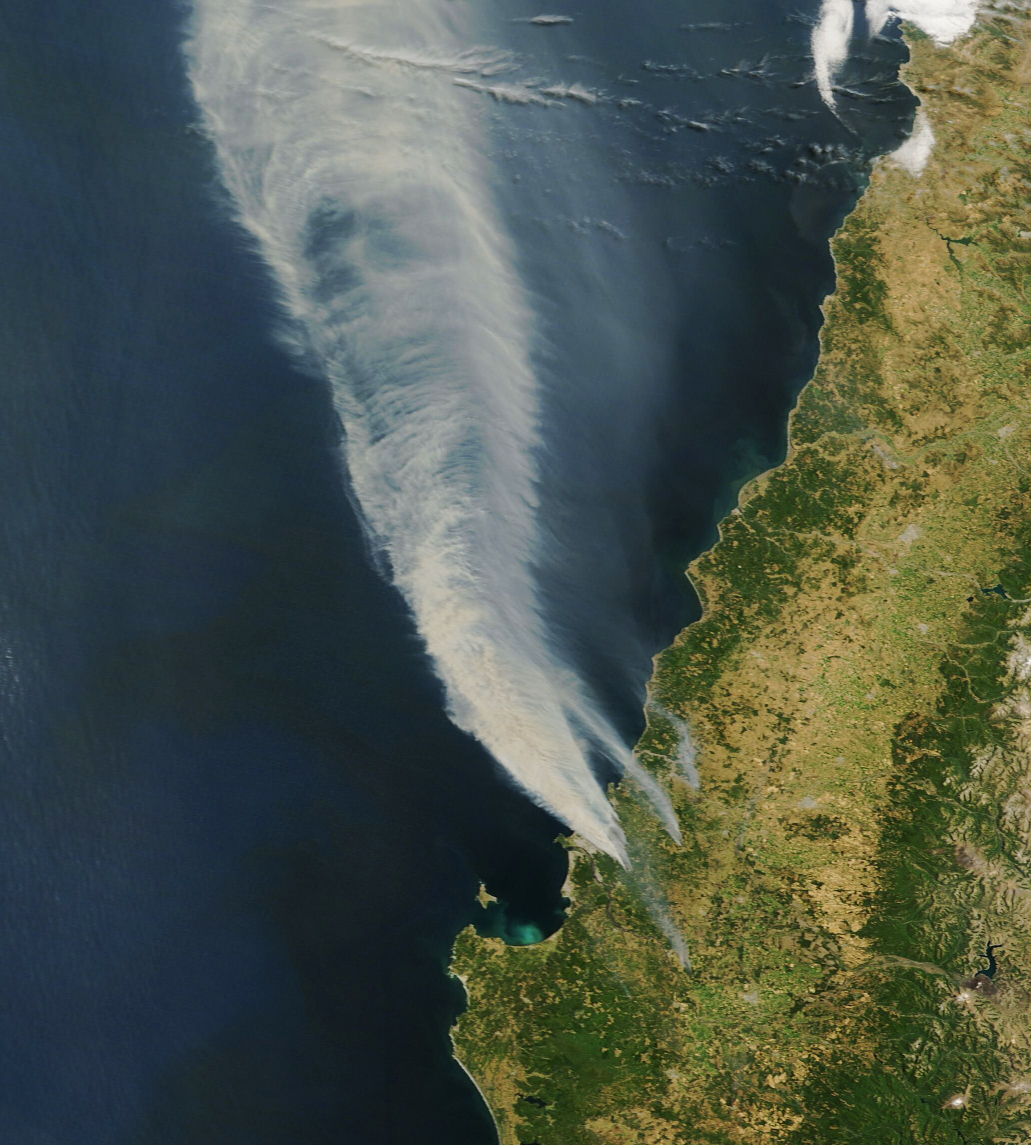
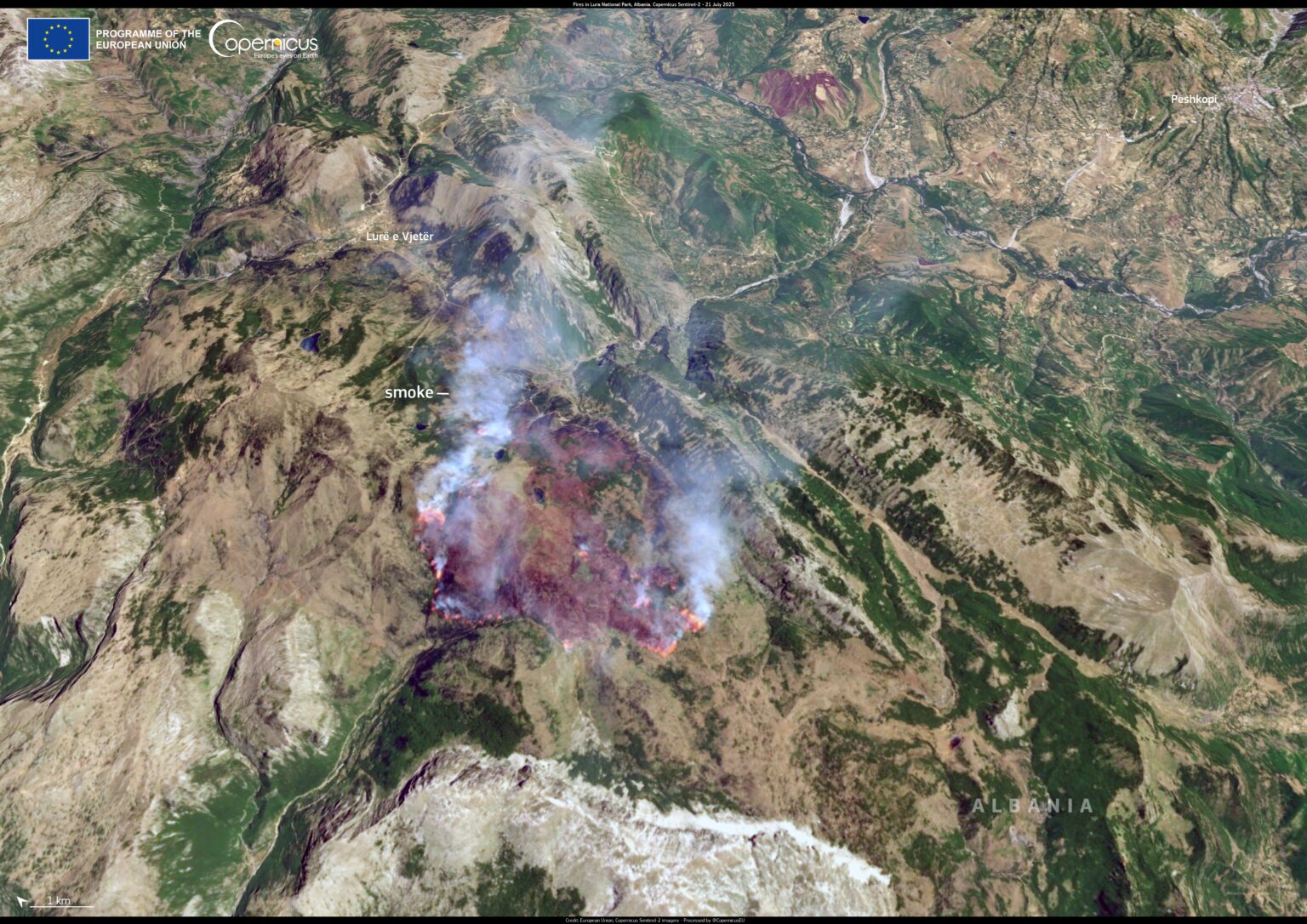
In mid-July 2025, the Albanian Ministry of Defense reported 18 wildfire outbreaks across multiple municipalities. The blazes have threatened residential areas and environmentally protected zones.